Did you know hair loss affects 80 million people in the US?
Which about 24% of the US population.
Yikes.
Thankfully, understanding and addressing it can mitigate the impact it has on your life.
This guide explores the different types, causes, stages, and treatment options available for men.
Buckle up.
Armed with knowledge, you can navigate this common issue with confidence and precision, ensuring you’re equipped to maintain your luscious hair, for the rest of your life.
Most importantly, you can get a plan in place so you don’t spend time worrying about it.
Let’s get to it.
But first, here is what you can expect.
Key Takeaways
- Hair loss affects over 80 million people in the U.S., which is approximately 24% of the population.
- Different types of hair loss include male pattern baldness, alopecia areata, telogen effluvium, and scarring alopecia, each with distinct causes and patterns.
- Understanding the stages of male hair loss, typically measured by the Norwood Scale, is crucial for effective treatment.
- Treatment options range from medications like Minoxidil and Finasteride to surgical procedures like hair transplants, laser therapy, PRP treatments, microneedlling, and exosomes.
- Adopting a hair-healthy lifestyle through nutrient-rich diets, stress management, and proper hair care can help prevent further loss and encourage regrowth.
- Losing your hair can significantly impact mental health, leading to decreased self-esteem and social anxiety, emphasizing the importance of addressing both physical and psychological aspects.
Understanding Hair Loss in Men
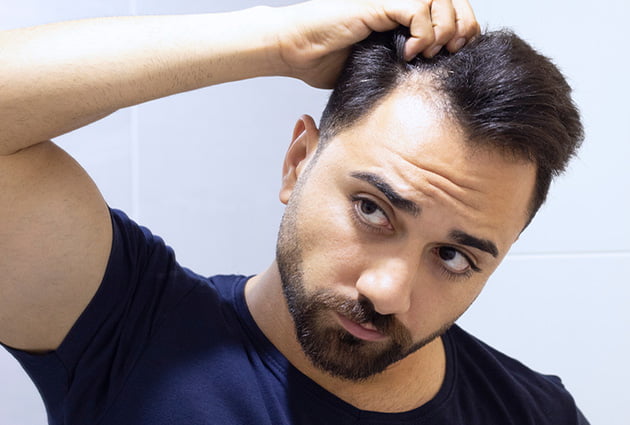

The Intricacies of Hair Growth and Loss:
Hair loss, scientifically known as alopecia, can significantly affect men’s psychological well-being and self-perception.
The condition primarily stems from genetic predispositions and hormonal changes, particularly due to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone, impacting hair follicles.
Basically, DHT is the enemy.
The Hair Growth Cycle: This natural process consists of three phases:
- Anagen (Growth Phase): Active hair growth lasting several years.
- Catagen (Transition Phase): Hair growth slows, and follicles shrink.
- Telogen (Resting Phase): Hair falls out, and new hair begins to form.
In a perfect world, this cycle would go on for eternity.
However, that pesky DHT we just talked about often has other plans.
Understanding these stages is crucial as disruptions can lead to hair thinning, receding hairlines, and baldness, mainly through male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia).
Identifying Root Causes of Hair Loss:
Beyond male pattern baldness, conditions like alopecia areata, telogen effluvium, and scarring alopecia also contribute to hair loss, triggered by factors ranging from autoimmune responses to stress.
Here is a quick breakdown of the most common types.
- Male Pattern Baldness (Androgenic Alopecia):
- Type: Non-scarring hair loss.
- Cause: Genetic predisposition and sensitivity to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
- Pattern: Receding hairline and thinning at the crown, often progressing to a horseshoe pattern of hair around the sides and back of the head.
- Common in: Men, but can also affect women.
- Alopecia Areata:
- Type: Non-scarring hair loss, autoimmune disorder.
- Cause: The immune system attacks hair follicles, often suddenly.
- Pattern: Round, smooth patches of complete hair loss, which can occur anywhere on the scalp or body.
- Common in: Both men and women, can occur at any age.
- Telogen Effluvium:
- Type: Non-scarring, temporary hair shedding.
- Cause: A shift in hair growth cycles, often triggered by stress, illness, hormonal change, or medication.
- Pattern: Generalized thinning of hair all over the scalp, not concentrated in one area.
- Common in: Both men and women, typically reversible.
- Scarring Alopecia (Cicatricial Alopecia):
- Type: Scarring hair loss, where hair follicles are destroyed and replaced with scar tissue.
- Cause: Can be caused by a variety of factors, including inflammatory skin conditions, infections, or other skin disorders.
- Pattern: Patchy hair loss with scarred areas on the scalp; hair does not regrow.
- Common in: Both men and women, but less common than the other types.
Each type of hair loss has its own set of treatments and prognosis, and the approach to treatment varies based on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition.
Key Contributing Factors:
- Genetics: A family history of baldness raises the likelihood of similar conditions.
- Health Conditions: Issues like thyroid disease, scalp infections, and alopecia types affect hair health.
- Lifestyle Influences: Diet, stress levels, and hair care practices play significant roles.
Identifying the Different Stages
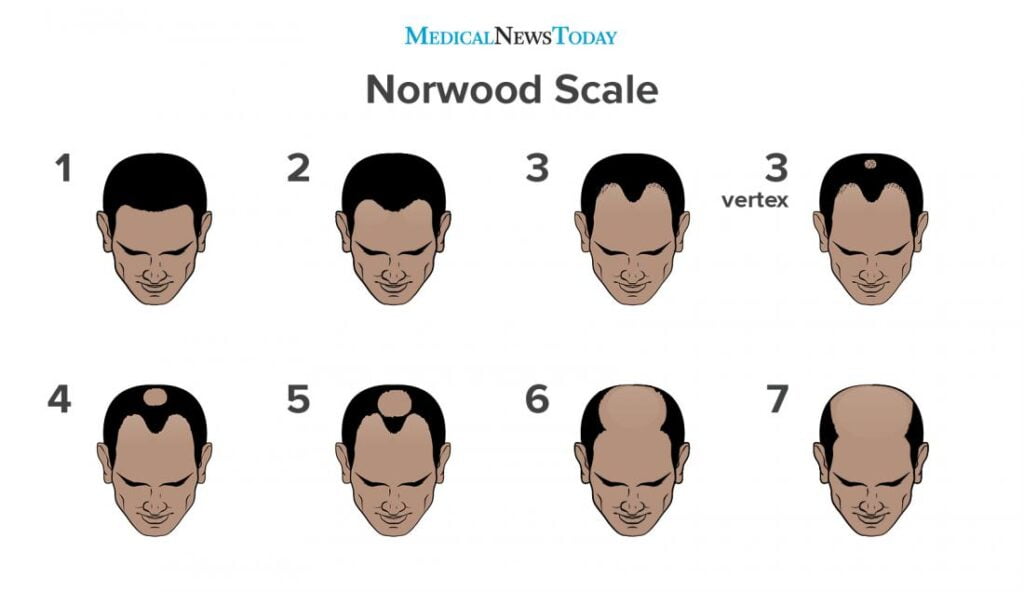
Understanding your hair loss stage, typically measured by the Norwood Scale, is crucial for effective treatment.
The scale ranges from minimal loss of hair to extensive baldness, providing a benchmark for classification and treatment strategies.
Warning Signs You (Might) Be Losing It:
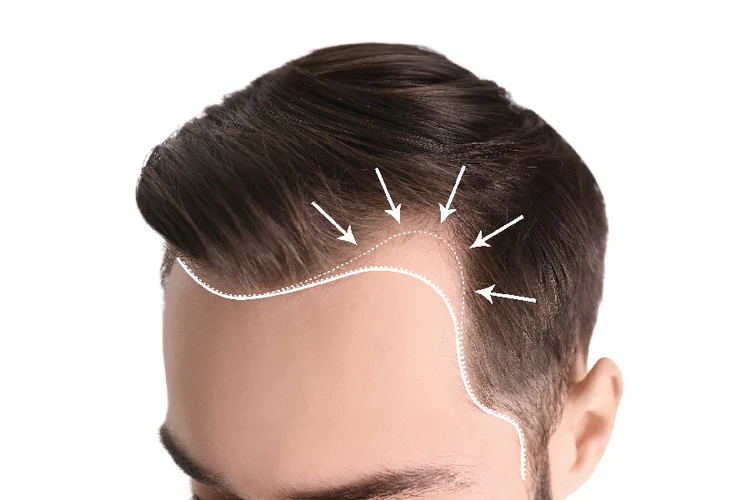
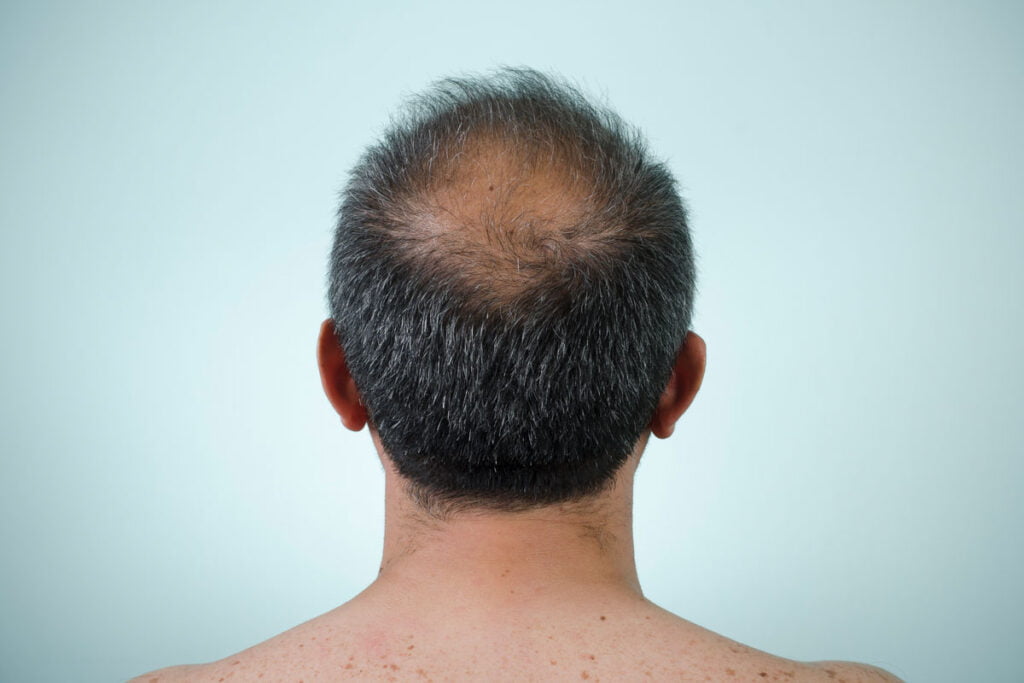
- Thinning hair atop the head.
- Receding hairline, notably at the temples.
- Visible scalp or bald spots.

Keep in mind, regular monitoring helps in early detection and intervention.
Potentially preventing any further loss of hair and increasing your odds of restoration.
Waging War on DHT
At this point we’ve covered the facts.
Odds are DHT will come for you when you least expect it.
But what if you could fight back?
Defend the front hair line.
And keep your hair for good.
The good news is you have options!

Conventional and Advanced Treatments
- Medications: Minoxidil and Finasteride are forefront treatments, slowing hair loss and promoting regrowth.
- Surgical Options: Hair transplant surgeries, like FUE (follicular unit extraction) and FUT (follicular unit transplantation), offer more permanent solutions.
- Emerging Technologies: Innovations such as laser therapy, PRP (platelet-rich plasma) treatments, and exosomes show promise in promoting hair growth.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a hair-healthy lifestyle can prevent further hair loss and encourage regrowth. Key changes include:
- Nutrient-rich diets supporting hair growth.
- Stress management techniques reducing hair loss triggers.
- Regular exercise promoting overall health and thereby influencing hair quality.
Hair Care and Maintenance
Proper hair care plays a pivotal role in preventing hair loss.
Certain hair care practices and products can contribute to hair damage and potentially speed up hair loss in men.
Especially for those who are already predisposed to conditions like male pattern baldness.
Here are some common factors to consider:
- Harsh Chemical Treatments: Regular use of hair dyes, bleach, relaxers, or chemical straighteners can weaken hair strands and lead to breakage. Over time, this can also affect the hair follicles.
- Tight Hairstyles: Consistently wearing hair in tight styles like ponytails, buns, or braids can pull on the hair and cause tension alopecia, a form of hair loss that results from constant pulling on the hair roots.
- Over-styling and Heat: Frequent use of heat-styling tools like hairdryers, straighteners, and curling irons can dry out hair, making it brittle and more prone to falling out. Over-styling or rough handling of wet hair can also cause breakage.
- Poor Nutrition: A diet lacking in essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals can lead to weakened hair and increased hair loss. Protein, iron, vitamins A, C, D, E, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids are particularly important for healthy hair growth.
- Over-washing and Harsh Shampoos: Washing hair too frequently, especially with harsh shampoos containing sulfates, can strip the hair and scalp of natural oils, leading to dryness and brittleness. This can exacerbate hair loss.
- Ignoring Scalp Health: Conditions like dandruff or psoriasis can lead to an itchy and flaky scalp, prompting scratching that harms the scalp and hair follicles. Using harsh scalp treatments or failing to treat these conditions can worsen hair loss.
- Excessive Stress on Hair: Physical stress from excessive weight or tension on the hair, and psychological stress from life events, can contribute to conditions like telogen effluvium, where more hairs enter the resting phase and then fall out.
To mitigate these risks, it’s recommended to adopt gentler hair care routines, avoid or limit harsh chemical treatments and heat styling, maintain a healthy diet, and manage stress levels.
If hair loss is a concern, consulting with a dermatologist or a trichologist (hair and scalp specialist) can provide personalized advice and treatment options.
Psychological Impact and Social Perceptions of Hair Loss

Hair loss can profoundly impact mental health, leading to decreased self-esteem and social anxiety.
Addressing these psychological effects is as crucial as treating the physical aspects.
Coping With Hair Loss
- Seeking Professional Help: Therapists and support groups can offer guidance and coping strategies.
- Community and Support: Connecting with others experiencing similar issues provides comfort and understanding.
The Future of Hair Loss Treatments: A Glimpse Ahead
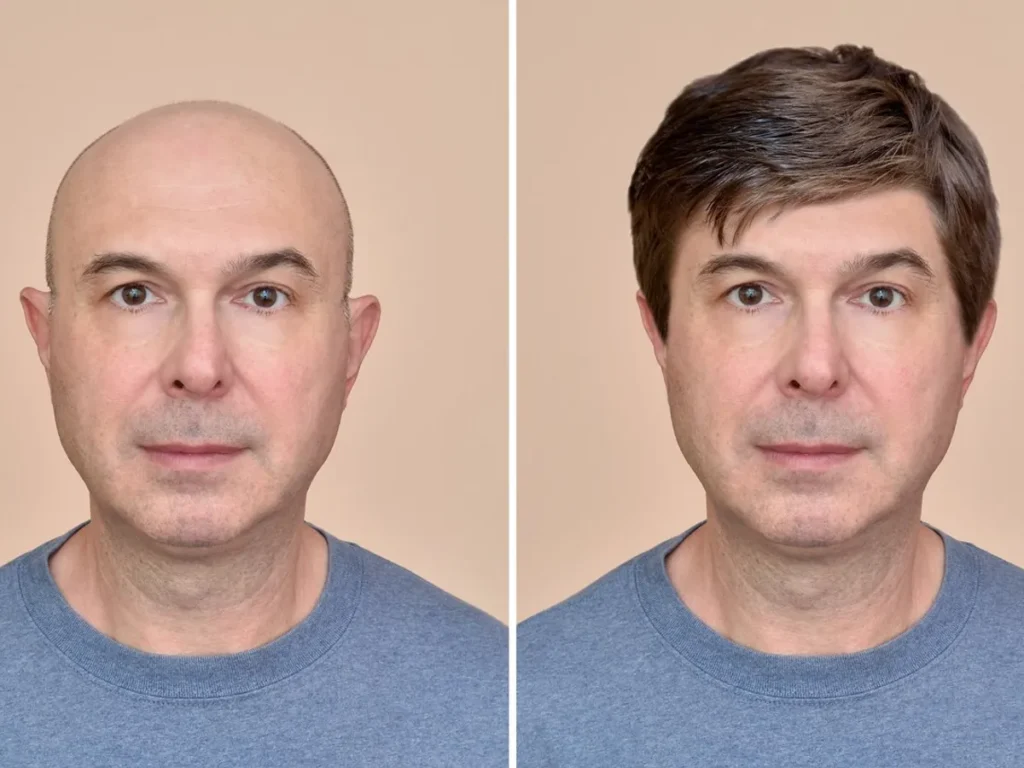

Research into hair loss is ongoing, with future treatments looking promising.
Advances in gene therapy, stem cell research, and cloning may offer new avenues for those experiencing hair loss.
Staying informed and consulting with healthcare professionals can help you navigate these options as they become available.
Conclusion
Hair loss in men is a prevalent issue, but with the right knowledge and approach, it can be managed effectively.
From understanding the underlying causes to exploring treatment options and coping with psychological impacts, this guide serves as a comprehensive resource for

